United Kingdom Economic Performance
Discuss about the economic performance of United Kingdom.
Introduction
The United Kingdom (UK) usually referred as the Great Britain is a developed country situated on the north-west coast of Europe. The UK is a sovereign state which is comprised of four countries namely; Scotland, England, North Ireland, and Wales. According to Mohan (2014), the state has a population of 65. 111 million which represents a yearly change of 0.61%. In the year 2014, the country recorded a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) and GDP per capita of 2.991.69 trillion and $ 40967.7 respectively (World Bank). United Kingdom faces numerous challenges related to the economy, state union, and how to make European Union (EU) operate in a manner that is consistent with the needs of the citizens.
The UK, a leading financial center, and trading power, is the third largest Economy in Europe after France and Germany (Sandford, 2015). However, the Great Britain’s economy faces various problem that makes it unstable and pushes it to recession. These include high consumer debt, declining home prices, and global economic slowdown. Vast strategies have been formulated to scale down the rampant economic slowdown attributed to declines in major industries such as manufacturing and banking (King & Fullerton, 2010). The design of these interventions aims at stimulating rapid economic growth and stabilizing financial market through measures such as suspending public sector borrowing and cutting taxes temporarily. The economy of UK encompasses the service sector, contributing to 78-percent of the GDP (World Bank).
Production/ Output Performance Analysis
According to Willett & Laney (2014), real GDP refers to a macroeconomic measure of the value of goods and services produced in a country for a given year corrected for inflation and other price changes. Real GDP measures the performance of the economy by indicating the market value of all goods and services produced by a given country during the period measure, including government purchases, personal consumption, private inventories, foreign trade balances and paid-in construction costs (Sandford, 2015). This economic indicator is usually expressed in percentage and the general consensus is that 2.5-3.5 percent annually in the real GDP represents a range of best overall benefit enough to offer cooperate benefits, provide jobs and maintain stability in all issues linked to inflation (Friedman & Schwartz, 2011). A value greater than 6-percent gives a negative perception regarding economic growth.
Gomes (2012) defines real GDP per capita as a ratio that indicates the average output of an economy per person by dividing the real GDP of a country by the total population. The ratio is used to compare the average output between countries by measuring the standards of living in the same currency. High standards of living translate to a high Real GDP per capital which is attributed to increased production in one or more sectors of the economy. Gomes (2012) affirms that an increase in per capita real GDP signifies a growth in the economy and thus, this indicator is commonly used as a measure of economic health for any given state.
Mohan (2014) defines real GDP growth rate as price adjusted nominal GDP distinguished against the real GDP for a period of one year. This rate measures economic performance by expressing the change in real GDP of two or more years in percentage. A positive change indicates a growing economy while a negative value depicts declining economic performance.
According to Gomes (2012), the Real GDP in the UK experienced sixteen consecutive years of growth prior to out fell in 2008 as a consequence of the global economic crisis. From the third quarter of 2010, the value of output has been increasing causing a regain in the levels that were in existence before the pre-downturn.
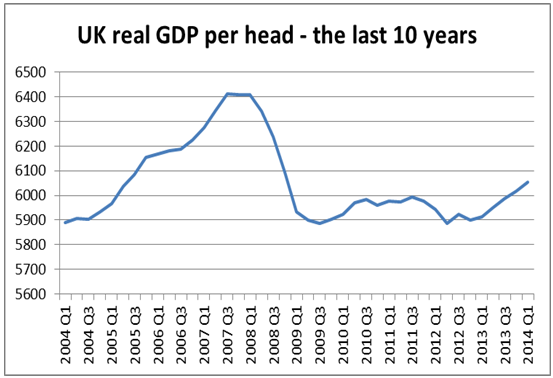
Fig 1. UK GDP Per Capita (US$) source: Cogley, Sargent, & Surico (2015). 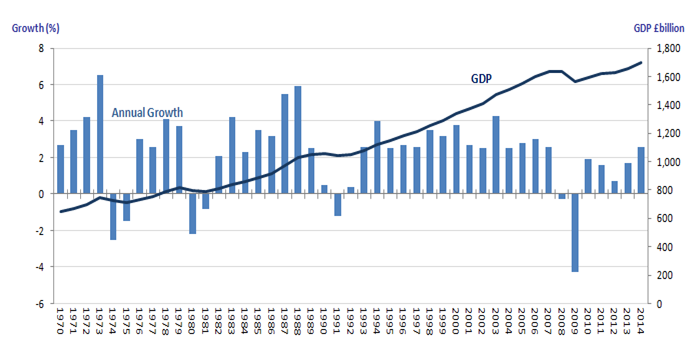
Fig 2. UK Real GDP growth rate in percentage. Source (Agénor & Canuto, 2015).
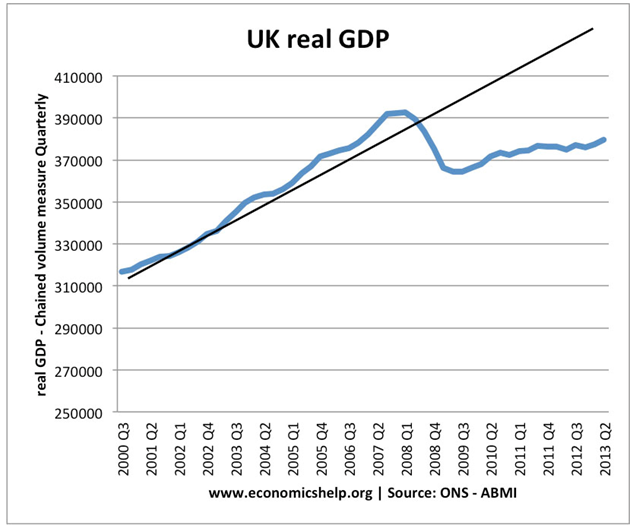
Fig 3. UK real GDP (US million $).
The UK has adopted various measures aimed at enhancing production output performance. According to Friedman & Schwartz (2011), the UK focuses on increasing aggregate and output demand as a measure of raising consumer spending and thus, ensuring sustainable economic growth. Alludes that the UK has formulated measures to steward growth in Real GDP through debt approach strategies. For instance, the government of the UK has adopted short-term public debt rather than long-term productivity which is considered unstainable and thus, creating possibilities of negative growth in the real GDP growth rate.
Labour Market Analysis
Clasen (2011) defines unemployment as a measure of the health of the economy that occurs when an individual who is actively seeking employment is not able to find it. Unemployment exists in three forms depending on the attributing reason and the long-term consequences to the economy. These forms include frictional, structural and cyclical unemployment. Willett & Laney (2014) ascertain that frictional unemployment occurs when there exists a mismatch between factors related to the employers and the employees. This type of job transition transpires when factors such as salary, skills, and benefits limits fruitful recruitment. Cyclical employment is attributed to economic recessions resulting to huge loss of job supply and thus, massive unemployment rates (Sandford, 2015). Structural unemployment transpires between job transitions arising due to dependency on high skilled labour that results in the rampant use of machines which attributes to massive loss of skilled labour. This type of unemployment is the most stimulus-resistant and permanent since its renders the qualifications and set skills of individuals obsolete.
United Kingdom unemployment rate has been changing insignificantly since 2000 standing at an average percentage of 5.4 percent. However, the rate increased to 8.4% in 2008 as a result of the global economic crisis that caused an economic recession in the kingdom. In 2014, the unemployment rate in the UK was at 6.4-percent, a value that outranked the global average of 6.0 at that time (Cogley, Sargent, & Surico, 2015). The high unemployment rate was linked to declining real GDP which was characterized by less production from the companies hence a less demand for workforce. Further, with falling GDP, some companies go out of business causing individuals to lose their jobs. According to Clasen (2011), 30-percent of the unemployment levels in the UK during this period was a consequence of low levels of confidence among investors caused by declining level of real GDP. This made firms reluctant to spend a substantial amount of capital in hiring new employees even at a lower wage.
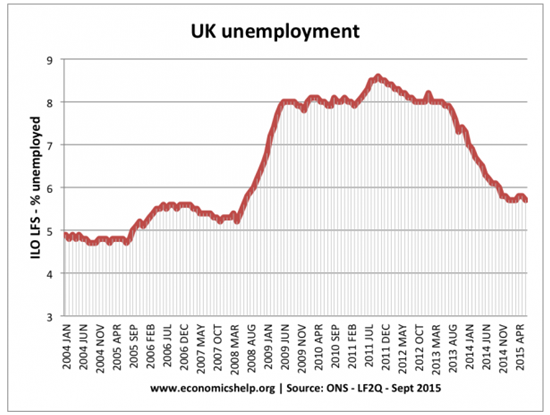
Fig 4. UK unemployment rate (%) 2004-2015.
Four types of unemployment are present in the UK economy. Clasen (2011) alludes that the greatest recession of 2008-2013 lead to cyclical unemployment due to high demand for employment in excess of the available positions. According to Friedman & Schwartz (2011), there is structural unemployment in the UK due to rampant changes in the nature of the economy especially decline in industries that were major contributors to economic growth. For instance, numerous jobs in manufacturing have been lost due to the incline of the economy to service sectors. Willett & Laney (2014) affirm that frictional unemployment in the UK is more pronounced than any other form of employment due to the longer time it takes the unemployed to secure job opportunities.
Various approaches have been adopted by the United Kingdom in order to improve the working of the labour market in matching individuals to the available employment opportunities. Cogley, Sargent, & Surico (2015) affirm that the UK formulated apprenticeship scheme policy aimed at equipping the unemployed individuals with new set skills that will aid them in finding employment and enhancing the incentives to find jobs. By the end of 2013, over half a million individuals had already started apprenticeships programs in the UK. The government of the UK has developed employment subsidies and tax cuts policies that aim at eradicating a frictional type of unemployment which is more rampant especially among the young people (Mohan, 2014). For instance, payment of up to £2,275 is offered to companies which employees individual aged between 18 and 24 years.
Price level Analysis
According to Friedman & Schwartz (2011), inflation is a continuous increase in the prices of goods and services that is expressed in percentage for given year. Demand-pull fluctuations that result in increased costs of scarce goods and services are the main attributes to inflation. The high-cost servers to scale down the purchasing ability of consumers and thus, ensure that the limited resources are available in the market (Agénor & Canuto, 2015). Clasen (2011) ascertains that surging prices of input resource are major causes of cost-push inflation that consequently results in higher prices for consumer goods and services. These production resources include the price of raw materials, salary increment, and import price fluctuations which are affected by the inconsistent strength of the currency.
Inflation rate gives a perception of how fast in terms of percentage a given currency losses its value in the global market. In the UK, Consumer Price Index (CPI) is usually used to give a perception of the inflation rate. United Kingdom’s inflation rate in the past decade has remained steady with a minimal deviation of either a drop or an increase of 0.3-percent (Burda & Wyplosz, 2012). However, this rate declined tremendously in 2008 reaching an all-time optimum value of 3.11 percent due to the global economic crisis that leads to economic recession. By the end of 2014, the UK inflation rate improved substantially from 2.83-percent in 2009 to 0.5-percent a move that is consistent with a target of below 2 that is cardinal towards enhancing production and pushing the aggregate demand upwards (Clasen, 2011). This increase was in accordance with the market expectation of 0.4-percent improvement that was attributed to declined transport and food prices.
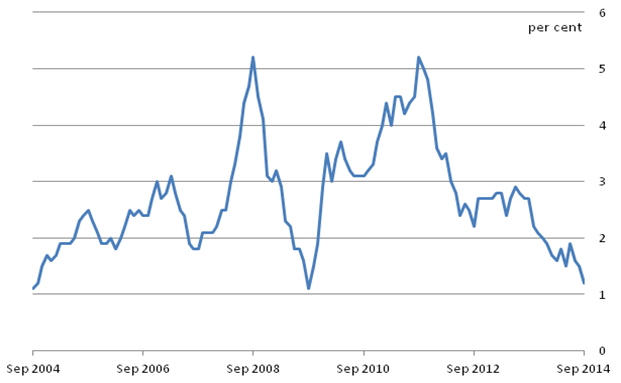
Fig 5. UK Inflation Rates in Percentage. Source: Cogley, Sargent, & Surico (2015).
Bowley (2016) argues that the cause of high inflation in the UK during 2011 was attributed to high temporary costs linked factors such as taxes, effects of devaluation and commodity prices. These factors increased the costs of operation in firms compelling them to increase the selling price of goods and services in order to make them remain profitable. According to Clasen (2011), cost inflation in the UK is caused primarily by the devaluation of 30-percent of all goods imported in the kingdom. Devaluation increases the cost of imports since it lowers the value of the pound and thus, firms and individuals have to pay more to acquire same imported commodities. The high price of oil is also a major factor leading to cost inflation. Oil is used as a primary raw material in the manufacturing and transportation of various goods in the UK. Willett & Laney (2014) allude that the cost inflation in 2008 was heightened by increases in the cost of oil by 20-percent causing a temporary spike in the price of goods and services.
Various measures have been developed by the UK in an attempt to counter the high prices of goods and services that lead to inflation. According to Burda & Wyplosz (2012), the UK formulated varied monetary policies which are set by MPC of the back of England and that serves to maintain low inflation. The functioning of these policies is stewarded by inflation targets set by the government for a given period of time. Baumol & Blinder (2015) ascertain that MPC employs interest-based strategies in maintaining low inflation and achieving the targets set by the government. For instance, increasing the interest rates scales up the cost of borrowing, a move that depresses attempts by consumers to borrow or spend money. Bernanke, Antonovics, & Frank (2015) ascertain that MPC increases interest rates in order to encourage saving and increase the cost of exchange rate consequently resulting in more exports and lower exports.
Conclusion
Evaluating the strength of an economy of a given country at any instant of time is significant in developing measures that can enhance economic growth and mitigates forces that slow down economic progress. The health of an economy is determined by a careful examination and analysis of various macroeconomic indicators that gives a general perception regarding the performance of varied sectors that contributes to economic growth. The commonly used indicators include unemployment rate, inflation rate, real GDP, real GDP growth rate and real GDP per capita. Evaluation of these indicators has depicted that the performance of the economy of the UK is strong in comparison to other countries in Europe. However, some indicators such as unemployment rate and high inflation rates give a deeper insight into the loopholes present in the economy. The UK has actively engaged in formulating interventions such as the monetary policies aimed at stabilizing the cost of goods, mitigating the challenges of unemployment especially among the young people, and increasing the real GDP.
References
Agénor, P. R., & Canuto, O. (2015). Middle-income growth traps. Research in Economics, 69(4), 641-660.
Ackermann, S. J., & Audretsch, D. B. (Eds.). (2013). The economics of small firms: A European challenge (Vol. 11). Springer Science & Business Media.
Astell-Burt, T., & Feng, X. (2013). Health and the 2008 economic recession: evidence from the United Kingdom. PLoS One, 8(2), e56674.
Baumol, W. J., & Blinder, A. S. (2015). Microeconomics: Principles and policy. Boston: Cengage Learning.
Bernanke, B., Antonovics, K., & Frank, R. (2015). Principles of macroeconomics. New York: McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
Bowley, A. L. (2016). Wages and Income in the United Kingdom since 1860. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Burda, M., & Wyplosz, C. (2012). Macroeconomics: a European text. Oxford: Oxford university press.
Clasen, J. (2011). The United Kingdom: towards a single working-age benefit system. Regulating the risk of unemployment: National adaptations to post-industrial labour markets in Europe, 15.
Cogley, T., Sargent, T. J., & Surico, P. (2015). Price-level uncertainty and instability in the United Kingdom. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 52, 1-16.
Friedman, M., & Schwartz, A. J. (2011). Monetary trends in the United States and the United Kingdom. National Bureau of Economic Research Books.
Gomes, P. (2012). Labour market flows facts from the United Kingdom. Labour Economics, 19(2), 165-175.
King, M. A., & Fullerton, D. (2010). The taxation of income from capital: A comparative study of the United States, the United Kingdom, Sweden and West Germany. University of Chicago Press.
Mohan, J. (2014). A United Kingdom?: economic, social and political geographies. Abingdon: Routledge.
Sandford, C. T. (2015). Economics of public finance: an economic analysis of government expenditure and revenue in the United Kingdom. Elsevier.
BoomGrades.com is
a name in assignment writing services that
students trust. We offer our assignment writing services for a wide variety
of assignment including essays, dissertations, case studies and more. Students can place
their order with us anytime as we function 24×7, and get their copies at
unbeatable prices. We guarantee that all of our solutions are plagiarism-free.



