Counselling Theories
Evolution of Psychotherapy and Contemporary Understandings of Counselling
Psychodynamic Theory focusses on all the unconscious aspects as they reflect in the Client’s present attitudes and behaviour. The objective of the psychodynamic theory is to help the Client become more aware of his present life and behaviour which could be as a result of his past experiences and reflections (Nathan & Gorman 2007). The psychodynamic approaches also help the Clients to self – evaluate any of their unresolved conflicts and issues which might have arised from their past experiences or relationships in order to transform their needs into better situations.
There are various approaches to psychodynamic theories like long term and short term approaches and their applications are also used to treat various disorders. The short – term psychodynamic therapies are used to treat various substance disorders and long – term therapies are used to treat more of the internal and human development related interactions.
The theories supporting the psychodynamic theories have originated and have been informed as psychoanalytic theories and there are 4 main segments of these theories called as Freudian, Ego Psychology, Object Relations and Self – Psychology.
Key Counselling Models
Psychotherapy theories and counselling models help the therapists with a clear framework to analyse and understand a Client’s behaviour and feelings where they help a Client’s therapeutic journey from the stage of a diagnosis to treatment (Roseman, Wiest, & Swartz, 1994).
Various Psychotherapy theories and counselling models which are used to treat most of the cases are
Psychoanalytic and Psychodynamic Theory
According to this therapy based on Sigmund Freud (1961), there are a lot of unconscious forces which have an impact on the behaviour of the person. As per this theory a person is allowed to talk to a therapist on a free basis without having to censor any of his feelings and dreams. (Freud, 1961). This therapy is still being used by most of the Psychoanalysts today.
By using this therapy, the Psychoanalysts can analyse the past relationships of a person and they can also analyse the present experiences of relationships of a person. It is believed that by discussing such aspects of a person’s life treatment and healing becomes a lot easier and can have a positive impact on the person’s life.
Behavioural Theory
Behavioural therapy is based on a belief that it is learnt and is practiced in life. There are two types of behavioural therapies where one of them is based on classic conditioning developed by Ivan Pavlov (1902) and B.F. Skinner who has developed another behavioural therapy approach called the operant conditioning.
As per the behavioural therapy by B.F. Skinner, power of rewards has seen a major rise in the behaviour and punishments have reduced the occurrence of a type of behaviour. (Leod, 2015).
Cognitive Theory
The Cognitive theory focusses on how a person’s thoughts can impact his own behaviour. This theory has a major focus on direct problem solving and the Cognitive Therapists also focus on a Client’s present situation and the issue they might be facing than their past (Mc Leod 2015). This form of therapy has gained a major focus in the present world as it helps cure a lot of conditions including mental anxiety, depression, personality disorders, anxious feelings and some of the abuse related issues.
Humanistic Approach
Human Therapists focus on their Client’s present issue and they in turn help their Clients achieve a highest solution from their present issue (Greenwald, & Banaji, 1995). Self – growth and self – actualisation are the critical factors which the Humanists focus on than on the past experiences and past relationships of a person.
Some of the examples of the Humanist therapies include the Gestalt and Client – Centered therapies.
These therapists help their Clients believe that they are in complete control of their own destinies and the Therapists treating the Patients show them that they genuinely care for them. Focussing on self – determination and self – responsibility are the 2 major factors which have a great influence on the people as per the humanistic approach (Pattyn, Verhaeghe, Sercu & Bracke, 2013).
Case
Jane is a 50 year old and has been suffering with loneliness in specific as her children moved away. Jane has been undergoing treatment for depression. There were a series of incidents which have been reported in Jane’s life like her Father’s death, Mother’s Accident and Husband’s separation. She also had a strong career as a Nurse which she had stopped practicing to care for her Mother.
As per the Psychodynamic and the Counselling theories, let us evaluate each of therapeutic modality to solve Jane’s case.
A Description of How Each Therapeutic Modality Might work with Jane
As per the Psychoanalytic and Psychodynamic theory, there are a lot of unconscious forces which have an impact on the behaviour of the person which is true in Jane’s case. She is being influenced by her past experiences and relationships which we can clearly see in her refraining to start her nursing career (Chua, Gonzalez, Taylor, Welsh & Liberzon, 2009). She is being occupied with the feelings that she might not be able to get retrained as per the new practice requirements.
As per the Behavioural therapy, it is based on a belief that it is learnt and is practiced in life. This is not in line with Jane’s life as nothing which she had gone through and which she is going through is something which she was trained on (Murphy, Cooper, Hollon & Fairburn, 2009). They were a series of life’s incidents which have happened in Jane’s life and each of those incidents has inhibited her from behaving in a specific way.
As per the Cognitive theory a person’s thoughts can impact his own behaviour. This therapy is very close to Jane’s life and it can be used in a subtle way to treat her. This theory as mentioned earlier has a major focus on direct problem solving and the Cognitive Therapists also focus on the Client’s present situation and the issue they might be facing than their past which can solve Jane’s issues and fears with which she has been restricting herself (Nathan & Gorman, 2007). This theory can also help Jane in curing her mental anxiety, depression, personality disorders and anxious feelings. 
Fig : Simply Psychology 2015
As per the Humanistic Approach, the Therapists focus on the Client’s present issue and they in turn help their Clients achieve a highest solution from their present issue. Self – growth and self – actualisation are the critical factors which the Humanists focus on than on the past experiences and past relationships of a person (Mc Leod 2011).
This therapy is also suitable to solve Jane’s issue where she can be brought out of her mental anxious state and can live by going back to her career.
A Summary of How Jane Could be Understood From the Perspective of the Respective Modalities
We could evaluate this from a perspective of the Cognitive approach and the Humanistic approach which are close to solving the Jane’s issue.
Cognitive Therapy can be used for direct problem solving and it can help focus on Jane’s present situation of fear and anxiety of getting back to work. This will also help her to free herself from all her inhibitions and can give her more strength to go out and meet people as she expressed that she wanted to have a relationship (Mc Leod 2015).
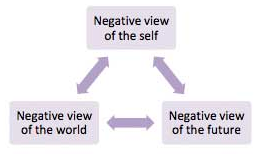
Fig : Simply Psychology 2015
Humanistic therapy can help Jane come out of her anxious state as the Therapist will focus on the her present issue and she can help Jane by advising her to take control of her own life which will help her realise her own potential and she can in turn go back to her Nursing career.
An Identification of Similarities and Differences Between the two Approaches in Working with Jane
Similarities
The therapies, Cognitive and Humanistic can help Jane conduct a self – evaluation than being helped by an external person. She can also realise her self – worth and strengths than imagining herself as a loser.
Differences
Cognitive therapy has to be essentially performed by an external person and the Humanistic approach can be learnt by the Patient herself and she can use it conduct a self – analysis whenever she requires it to be performed.
Most Appropriate Approach for Working with Jane
The most appropriate approach for working with Jane would be the Humanist Approach as she tends to be an introvert and a person who could be susceptible to external fears and worried than strengthening herself from within.
Jane is filled with the cognitive triad as mentioned earlier where she imagines herself to be helpless and critical which is not as per her case. She is typically a person who can get depressed with the negative thoughts about herself and about how the world would perceive her. By using the humanistic approach these negative thoughts can be over ruled and can help Jane overcome such feelings and can also help her become more successful.
References
Chua, H. F., Gonzalez, R., Taylor, S. F., Welsh, R. C., & Liberzon, I.(2009). Decision-related loss: regret and disappointment. Neuroimage, 47(4), 2031-2040. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.06.006
Freud, S. (1961). The resistances to psycho-analysis. In The Standard Edition of the Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud, Volume XIX (1923-1925) (pp. 211-224): The Ego and the Id and other works
Greenwald, A. G., & Banaji, M. R. (1995). Implicit social cognition: attitudes, self-esteem, and stereotypes. Psychological review, 102(1), 4
McLeod, S. A. (2013). Sigmund Freud. Retrieved from www.simplypsychology.org/Sigmund-Freud.html
Mc Leod, S. (2015). Cognitive Behavioural Therapy. Simply Psychology. Retrieved on August 25th 2016. http://www.simplypsychology.org/cognitive-therapy.html
Mc Leod, S. (2011). Bandura – Social Learning Theory. Retrieved on Aug 26th 2013. http://www.simplypsychology.org/bandura.html
Nathan, P. E., & Gorman, J. M. (2007). A guide to treatments that work (3rd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press
Pigott, H. E. (2011). STAR*D: A tale and trail of bias. Ethical Human Psychology and Psychiatry, 13, pp. 6–28
Murphy, R., Cooper, Z., Hollon, S. D., & Fairburn, C. G. (2009). How do psychological treatments work? Investigating mediators of change. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 47, pp. 1–5
Pattyn, E; Verhaeghe, M; Sercu, C. ; Bracke. (2013). Social Psychiatric epidemiology, Vol.48 (10), pp. 1637-1645 (Peer reviewed Journal)
Roseman, I.J., Wiest, C., & Swartz, T.S. (1994). Phenomenology, behaviors, and goals differentiate discrete emotions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67, 206±211
BoomGrades.com is known for providing well-regarded coursework writing services that exactly meet the students’ needs. Our each assignment is customized as per the provided guidelines and maintains originality involving latest information on the researched topic. Hence, students receive 100% plagiarism-free top-quality well-structured coursework help solutions from us. In addition, we offer 24×7 live support to ensure that students get uninterrupted coursework writing help when they need it most.



