Global Greenhouse Gases
Discuss about the Global Greenhouse Gases.
Introduction:
1. Global greenhouse gases are responsible for the rising incidence of global warming which is leading to the grave issue of climate change. One of the main contributors of global greenhouse gases is through the use of various fossil fuels which is particularly high amongst the OECD countries and Australia is one of these countries. In case of Australia, this becomes even more significant since Australia is bestowed with a plethora of minerals particularly coal. Due to abundant availability of coal, it is widely used for the generation of electricity which is a significant contributor to greenhouse gases along with the exhaust from automobiles. Additionally, mining as an industry is quite substantial in Australia with two mining global giants i.e. BHP Billiton and Rio Tinto having significant operations based in Australia (Milman, 2013).
The contribution to the greenhouse gases by Australia along with the sector wise breakup of contributors is shown below (Hannam, 2015).
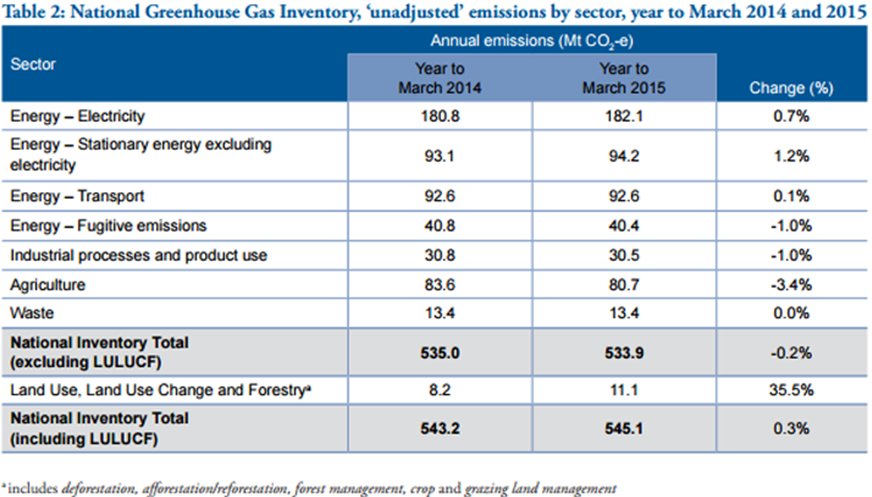
Further, the historical trends of Australia with regards to greenhouse emissions is summarised in the table below (Hannam, 2015).
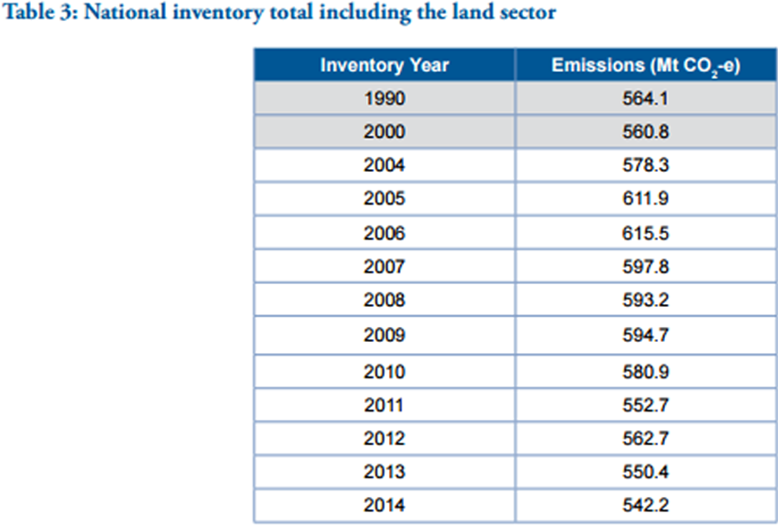
It is apparent from the above statistics that despite the Kyoto Protocol, there has not been a significant decline in the carbon emissions and in the recent years performance in this regard has been lacklustre. In terms of annual greenhouse emissions, Australia contributes about 1.3% to the total global emissions. For a country with very small population, clearly this is a very high contribution and therefore it is imperative that going forward prudent measures need to be taken to manage greenhouse emissions (Milman, 2013).
2. Australia’s per capita emissions stands at 17.3 tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent. In comparison, the corresponding values for India and China stand at 1.8 tonnes and 7.6 tonnes respectively (WorldBank, 2014). It is apparent from the above statistics that the energy usage per person is comparatively very high in Australia as compared to India and China. This may be attributed to the difference in levels of development as Australia is a developed nation and has a higher per capita income levels in comparison to the developing nations i.e. India and China. Due to higher income levels of an average Australia, there is higher propensity to consume energy in various forms (Milman, 2013). This is clearly not possible in India and China where a substantial part of the population lives below the poverty line and hence has little access to various energy resources. In these nations, major energy is used by the middle class and the rich class which contribute to greenhouse emissions. It is imperative considering the above statistics that Australia in global interest must take requisite measures to limit the emission of these greenhouse gases.
References
Hannam, P 2015, Paris 2015: Australia’s greenhouse gas emissions show ‘disturbing increase’ amid record global heat, The Sydney Morning Heerald, Available online from http://www.smh.com.au/environment/un-climate-conference/paris-2015-australias-greenhouse-gas-emissions-show-disturbing-increase-amid-record-global-heat-20150821-gj4nl7.html (Accessed on July 28, 2016)
Milman, O 2013, Australia worst carbon emitter per capita among major western nations, The Guardian, Available online from https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2013/nov/19/australia-worst-carbon-emitter-per-capita-among-major-western-nations (Accessed on July 28, 2016)
WorldBank 2014, CO2 emissions (metric tons per capita), The World Bank, Available online from http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/EN.ATM.CO2E.PC (Accessed on July 28, 2016)
BoomGrades.com is
a name in assignment writing services that
students trust. We offer our assignment writing services for a wide variety
of assignment including essays, dissertations, case studies and more. Students can place
their order with us anytime as we function 24×7, and get their copies at
unbeatable prices. We guarantee that all of our solutions are plagiarism-free.



